Rubber Pinch Roller Revitalization
The Essential Role of Rubber Pinch Rollers in Industrial Machinery
Rubber pinch rollers are unsung heroes in manufacturing and printing industries, responsible for guiding materials with precision. These cylindrical components, often paired with metal rollers, apply controlled pressure to feed paper, fabric, or film through machines. Their rubber surfaces provide grip without damaging delicate substrates, making them indispensable in processes like web printing, laminating, and textile production. Over time, however, exposure to friction, heat, and chemicals degrades their performance—which is why revitalization matters more than ever.
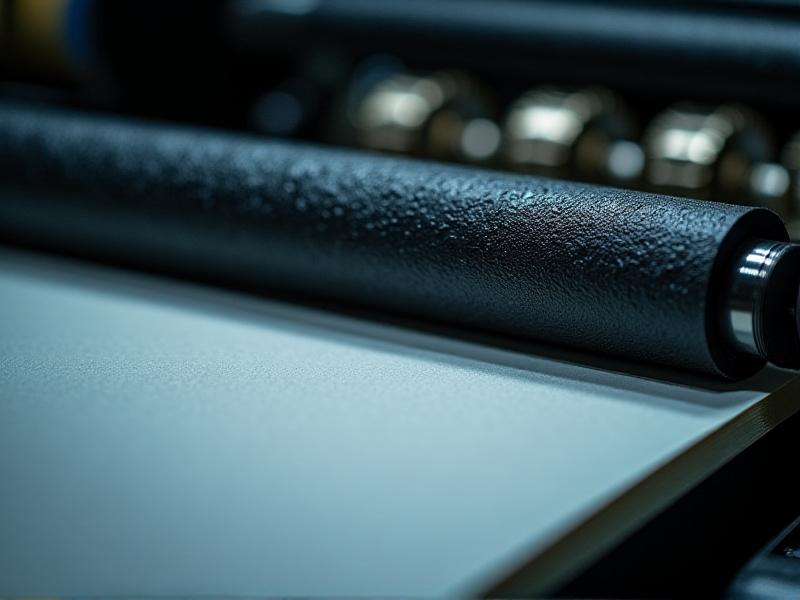

Identifying Signs of Pinch Roller Degradation
Recognizing early symptoms of wear can prevent costly downtime. Common red flags include visible cracking, flat spots, or a glazed surface texture. Operators might notice inconsistent material feeding, slippage, or unusual noise during operation. In printing, degraded rollers often leave streaks or smudges. A simple “thumb test”—pressing into the rubber to check for resilience—can reveal hardening or loss of elasticity. Proactive monitoring through these indicators allows teams to schedule maintenance before catastrophic failure occurs.
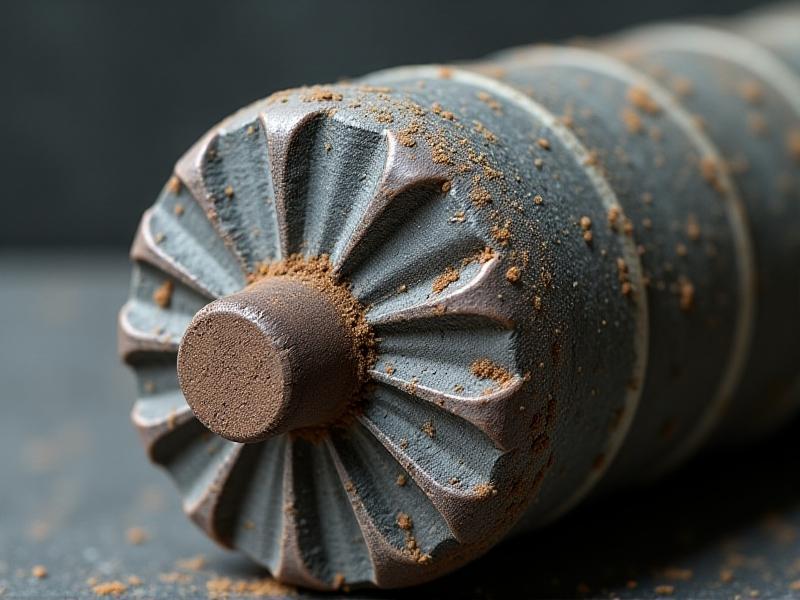

The Science Behind Rubber Pinch Roller Revitalization
Revitalization extends roller life by restoring surface properties through mechanical and chemical methods. Techniques range from abrasive blasting to remove hardened layers, to specialized solvent cleaning that rejuvenates rubber compounds. Advanced shops use lathe-based precision grinding to recreate original tolerances, followed by application of UV-resistant coatings. Recent innovations include cryogenic treatments that reverse plasticizer loss by deep-freezing rollers, effectively “resetting” the rubber’s molecular structure.
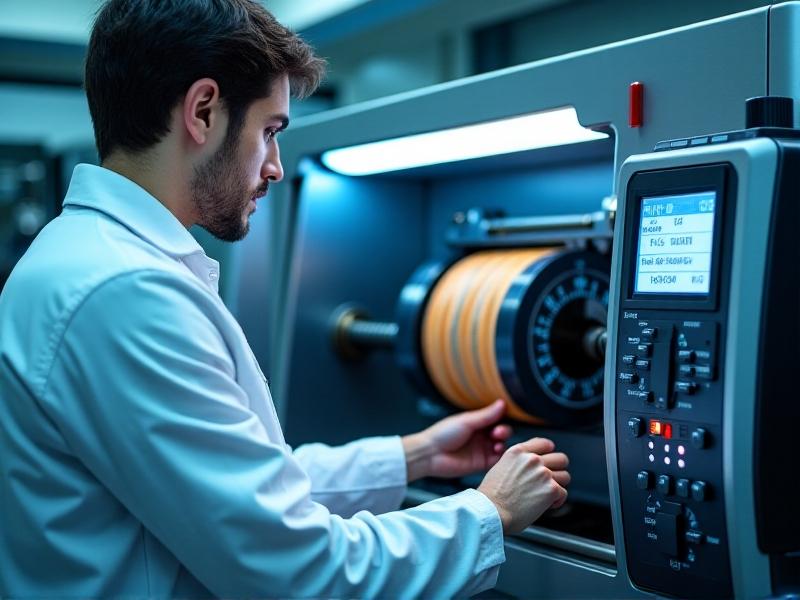

Cost and Environmental Benefits of Revitalization
Replacing a 24-inch industrial pinch roller can cost upwards of $3,000, while professional revitalization typically costs 40-60% less. Beyond immediate savings, revitalization keeps rubber out of landfills—a critical consideration as industries face stricter sustainability mandates. Case studies show a Midwestern packaging plant reduced roller-related waste by 72% over five years through planned revitalization cycles, simultaneously cutting annual maintenance budgets by $180,000.

Proactive Maintenance Strategies for Extended Roller Life
Implementing a six-month inspection protocol can triple roller lifespan. Key practices include using pH-neutral cleaners to avoid rubber breakdown, storing rollers vertically on climate-controlled racks, and maintaining detailed logs of hardness measurements. For critical applications, portable durometers allow on-site Shore A hardness testing. Leading plants now use IoT-enabled vibration sensors to detect microscopic surface changes long before visible wear appears.
Emerging Technologies in Roller Rehabilitation
The field is being transformed by AI-driven surface analysis software that predicts optimal revitalization timing, and nanoparticle-infused coatings that reduce friction coefficients by 30%. Experimental plasma treatment systems now modify rubber surfaces at the molecular level without material removal. Meanwhile, biodegradable revitalization gels made from modified plant oils offer eco-friendly alternatives to traditional chemical baths, aligning with circular manufacturing principles.